Save to My DOJO
Task Scheduler is a built-in Windows utility that does not often get the respect it deserves as a powerful automation tool. Although it only has a few features, Task Scheduler’s ability to run any script at a scheduled time or be triggered via an event is very useful!
This blog will show you how you can utilize Task Scheduler to make your backups and recoveries more successful, even if you use a basic utility like Windows Server Backup. In fact, even Windows Server Backup, along with other leading backup providers like Altaro, will use the Task Scheduler engine’s via calling the TaskSchd.h APIs.
This blog will show you how you can use Task Scheduler to automate your backup, recovery, and administrative tasks before you even need to start the backup itself.
Task Scheduler for Backups Overview
Let’s review a few relevant features of Task Scheduler, which can be used to improve your backup and recovery procedures:
- Trigger – This defines an action or time which causes a task to begin. There are two trigger types we can use, including:
- On a schedule – This will let you run a task at a specific time daily, weekly or monthly, such as creating a daily backup. You can also repeat the task multiple times a day in increments of 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes, or once an hour.
- On an event – This trigger will let you run a task if a specific event is detected in an event log, such as a failed backup attempt.
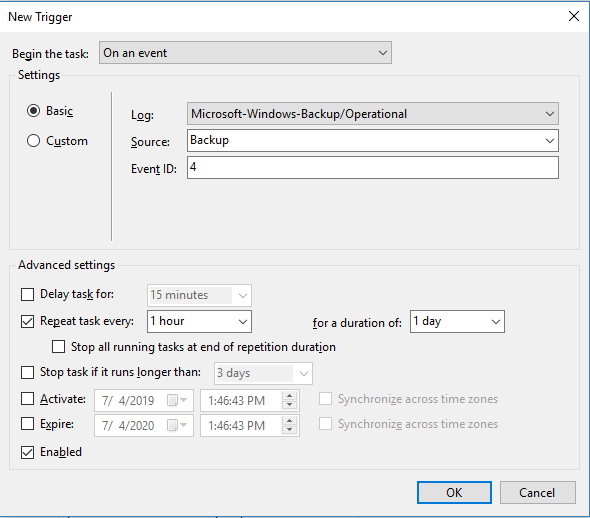
Figure 1: Task Scheduler is configured to trigger an action if Event 4 (Backup Successful) is written to the event log.
This task will then monitor the event log, and if a matching Event ID is discovered, it will trigger an action.
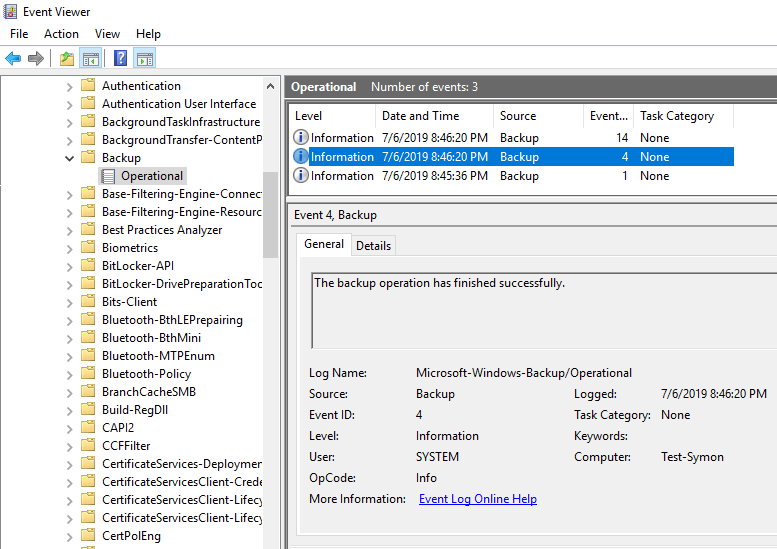
Figure 2: Event Viewer detects a backup event and causes Task Scheduler to trigger a task.
- Action – This defines what happens once the task is triggered.
- Start a program – this is almost always used when a task is triggered. It will either start a program or run a script, so you can use this to launch your backup provider once your prechecks have passed. Since you can run any program with a command-line interface, it gives you the flexibility to use traditional scripting languages or PowerShell. You can also send files or pass variables into these scripts.
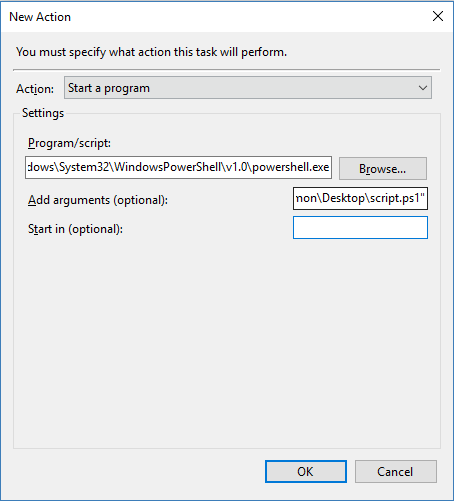
Figure 3: Task Scheduler is triggered to run PowerShell and then provide the location of a script
- Send an email – This feature will connect to an SMTP mail server and send an email to an administrator. Microsoft has deprecated support for this feature, which means that it should work, but Microsoft will not update it and no longer provides technical support for it.
For additional information about Task Scheduler, visit Microsoft’s documentation About the Task Scheduler.
Running a PowerShell Script with Task Scheduler
Since Windows Server uses PowerShell as its primary scripting language, this section offers guidance for running PowerShell from Task Scheduler. If you are integrating your script with any third-party API, such as your backup provider, you should ensure that they have an API or PowerShell cmdlets that you can use to automate your backup tasks. Altaro offers both an API and PowerShell, making it easy to perform various automated tasks, such as applying a configuration template, taking an offsite copy, and restoring a VM.
For any task which requires you to run a PowerShell script, you have to be able to launch PowerShell and send it the file path of the script to run. For Windows or Windows Server, you will usually use the following parameters from the Start a program option:
- Program/script:C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
- Add arguments:
- Cmdlet such as Start-WBBackup -Policy $Policy -Async
- File location such as C:\Users\Admin\Scripts\Backup\backup.ps1
- Start in: Directory location to start the command prompt, such asC:\Users\Admin\Scripts\Backup\backup.ps1
If you are using Windows Server Backup with PowerShell, you can find complete documentation here.
Creating a Backup with Task Scheduler
The first collection of tasks you should consider are related to creating a backup. While every backup provider offers this fundamental feature, they may not allow you to automate pre-backup testing and post-backup verification tasks. Remember that for a backup to be completed successfully, dozens of sequential actions need to happen correctly before and after the backup. You can use the following checklist against your system, but be sure to consider any other custom steps in your standard backup workflow. The order suggests which actions can be run concurrently (1a,1b, etc.) and should be consecutive (4,5, 6, etc.), but you should reorder to whatever makes sense for your infrastructure. The backup process can be triggered by either a manual request, an event, a previous task, or a scheduled time.
| Order | Component | Type | Trigger | Action |
| 1a | Storage | Backup storage health check | Backup started | Test storage is online & healthy
Test disk has available space |
| 1b | Virtual Machine | VM health check | Backup started | Test VM is online & healthy
Test backup provider has access to guest OS or VHD |
| 2a | Application | Application health check | VM health check completed | Test application is online & healthy |
| 2b | VSS Writer | VSS health check | VM health check completed | Test VSS writer is online & healthy |
| 2c | Backup Software | Backup software health check | VM health check completed | Test VSS provider is online & healthy |
| 3a | Network | Network availability check | All health checks complete | Test backup network is online
Test backup network has bandwidth |
| 4 | Network | Optimize network access | Network availability check complete | Prioritize traffic in your virtual and physical networks for the backup network and its traffic using QoS and network prioritization |
| 5 | Backup Software | Start Backup | Optimize network access complete | Start the backup. The provider should take care of application-level tasks such as quiescing the traffic. |
| 6 | Backup Software | Monitor Backup | Error during backup | Monitor the backup provider’s event log
Send a message to the admin |
| 7 | Backup Software | Verify Backup | Backup Complete | Send a message to the admin |
| 8 | Network Prioritization | Deoptimize network access | Verify backup complete | Deprioritize traffic in your virtual and physical networks for the backup network and its traffic using QoS and network prioritization |
| 9 | Compliance | Document Backup | Verify backup complete | Document that the backup completed through your compliance procedure |
Managing your Backups with Task Scheduler
Task Scheduler can help you with regular backup management and maintenance tasks. Most enterprise backup providers will provide similar functionality, such as Altaro’s VM Backup, which allows you to replicate your backups to Microsoft Azure.
| Component | Type | Trigger | Action |
| Storage | Available space for backups | At regular intervals and before each backup, verify there is enough free disk space. | Send an alert/email to an admin or automatically procure additional storage. |
| Storage | Replication | On a schedule or after a successful backup | Replicate backup file to a secondary or offsite storage location |
| Compliance | Backup retention | If a backup is no longer needed or must be deleted after a certain time | Delete the backup |
Triggering a Recovery from Backup with Task Scheduler
Whenever there is an outage, you will want to verify which services were affected and whether any data loss happened. While these tests are running, you may want to also initiate parts of the recovery process so that you can minimize the total service outage. It is important to automate the detection and recovery because any manual steps will slow down the process. You can find more best practices from Altaro’s blog about how to Recover and Restore your Backups Faster after a Disaster. The following order and steps may vary based on your infrastructure and recovery solution.
| Order | Component | Type | Trigger | Action |
| 1 | Monitoring Software (SCOM or Event Log) | Failure detection | Failure event detected | Verify failure
Send alert/email to an admin Verify data loss |
| 2a | Monitoring Software (SCOM or Event Log) | Failure verification | Failure event verified | Send alert/email to an admin |
| 2b | Monitoring Software (SCOM or Event Log) | Failure verification | False failure detected | Cancel the recovery process |
| 3 | Backup Software | Verify data loss | Failure verification | Determine whether data loss is acceptable, or to use the last good backup |
| 4 | Backup Software | Find the best backup | Data loss determined | Find the best available backup |
| 5 | Storage | Prepare storage | Backup ready for recovery | Determine the fastest media
Prepare server or VM storage for recovery file |
| 6 | Network | Network availability check | All health checks complete | Test backup network is online
Test backup network has bandwidth |
| 7 | Network | Optimize network access | Network availability check complete | Prioritize traffic in your virtual and physical networks for the backup network and its traffic using QoS and network prioritization |
| 8 | Backup Software | Recover backup | Storage ready for recovery | Restore backup to server or VM |
| 9 | Virtual Machine | Create VM | Recovery storage ready | Attach disk for recovery file
Provide VM specification, increase the startup memory, increase the VM priority Create VM Start VM |
| 10 | Application | Start application | VM ready | Start the restored application |
| 11 | Backup Software | Verify recovery is successful | Application ready | Send alert/email to an admin |
| 12a | Network Prioritization | Deoptimize network access | Verify recovery is successful | Deprioritize traffic in your virtual and physical networks for the backup network and its traffic using QoS and network prioritization |
| 12b | Compliance | Post-Recovery Triage | Verify recovery is successful | Collect all event logs and other data required for failure analytics |
If, at any time during this process, you need to terminate a task that is running, such as detecting a false failure alert, you can use the PowerShell cmdlet to stop any Task Scheduler task. Keep in mind that this will terminate the task only if it is still managed by Task Scheduler. If this task has already triggered some other action, such as running a PowerShell script, then that other process must also be terminated.
Task Scheduler offers simple yet powerful tools for managing backups and recovery. Whether you depend on Task Scheduler or a third-party backup solution to manage your critical data, make sure that your backup infrastructure is also highly-available and resilient. Windows Server Task Scheduler can even be deployed on a Failover Cluster so that its tasks failover between nodes and will always run. Check out the documentation on how to use PowerShell to manage Clustered Scheduled Tasks. With these Task Scheduler tips and tricks, you will now be able to add more resiliency to your backup and recovery workflow.

Not a DOJO Member yet?
Join thousands of other IT pros and receive a weekly roundup email with the latest content & updates!









